
![]()
AVSS + Windows + Internet = AVSS/
![]()
The AVSS software is
based on the M Technology, a programming
language, database manager, and operating system. Advanced for its time, M has
had multi-user and multi-tasking capabilities in the DOS environment since the
1980s. These capabilities facilitated automatic communications between AVSS
computers, as, for example, between hospitals and local health departments. The
M operating system, however, required complete control over critical computer
resources in order to accomplish this goal and the M database manager required
a dedicated environment to insure its integrity. This meant that AVSS
PCs had to run on a DOS 6.22 computer dedicated solely to AVSS. With the advent of
Windows, this approach, though once reliable and effective, became increasingly
outdated. Yet, attempting to run
DOS-based AVSS on Windows computers was not recommended and the AVSS
Project did not support this approach.
In 2001, in response to this situation, the AVSS Project developed a client-server approach using the Internet
and SSH encryption that allowed users to securely run AVSS on a Windows
workstation. This combination is
referred to as AVSS/NET. By using
an AVSS/NET client workstation, users
saw the same, familiar interface as with the DOS version so that there was no
need for retraining. Additionally,
analysts could easily and securely download AVSS/
By April 2006 all 56 AVSS local registration districts had converted to AVSS/
1. AVSS/
1. Windows-based so that an AVSS workstation can run other
applications such as word processing.
2. Eliminates the need for aging, obsolete hardware and dedicated telephone
lines.
3. Eliminates system management responsibilities such as backups and hardware
maintenance.
4. More reliable and faster.
5. Eliminates the need to for local staff to perform annual AVSS
updates.
6. Streamlines the downloading of data from AVSS
to other software and makes AVSS data
more accessible.
2. AVSS/
AVSS/
1. Windows 2000/XP workstation (not Win9x or NT).
2. Continuous (not modem-based) Internet access with Port 22 open and with on-site
3. HP
LaserJet 2300 printer or equivalent (see Manual
for more details). Note: Do NOT
use the InkJet version.
4. Licensing fees of $550 per
workstation every three years (these supplant the current fee of $250 every 3
years).
5. A deployment
plan involving all users in a local registration district converting to
AVSS/
3. AVSS/
SSH (Secure SHell): SSH is a secure protocol that replaces existing
Client Workstation: A Windows 2000/XP workstation that can connect to
the Internet via a local
Encryption Server: A UNIX computer running SSH. This server provides
users with secure login connections, file transfer, and
AVSS Server: A Windows XP server running AVSS for Windows
with Telnet support connected to the Encryption Server with a private address.
4. AVSS/
AVSS/
1. Viewing the content and
type of communication by anyone other than AVSS/
2. IP Spoofing, where a remote host sends out packets that pretend to come from
another, trusted host.
3. IP source routing, where a host can pretend that an IP packet comes from a
trusted host.
4. DNS spoofing, where an attacker forges name server records.
5. Interception of clear text passwords and other data by intermediate hosts.
6. Manipulation of data by persons in control of intermediate hosts.
By placing the AVSS Server in a private network, outside access is
locked out. The only way to access the AVSS Server is either directly by
means of the AVSS Server console or indirectly by using a SSH
Workstation through the Encryption Server, i.e., by using AVSS/
5. AVSS/
Both the Encryption
Server and AVSS server sit behind an
IP based packet filtering firewall. All incoming and outgoing packets are
inspected and analyzed. IP spoofing is prevented by only allowing packets that
have identical incoming and outgoing destinations. The firewall also prevents
6. AVSS/
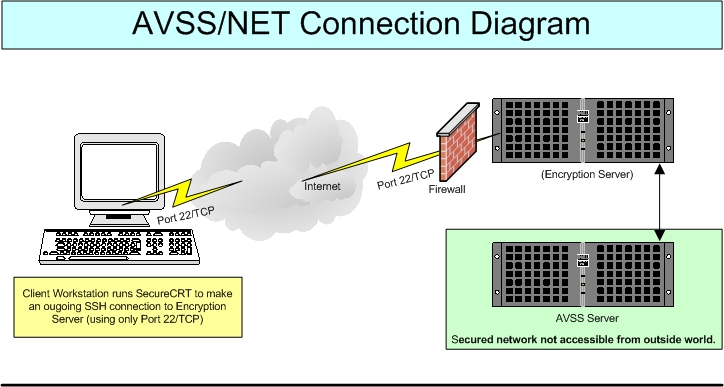
As shown in the AVSS
connection diagram below, the AVSS/
The Client Workstation loads the SSH software (SecureCRT)
and tries to make a connection to the Encryption Server. The Encryption Server
checks its database to see if the Client Workstation is coming from a trusted
source then prompts the Client for authentication. When the Client Workstation
successfully connects to the Encryption Server, the Encryption Server then
connects to the AVSS Server. The user is then prompted for their current
AVSS password and normal AVSS
operations can begin.
![]()
